EDI Water Systems/Deionised / Demineralised
One Eight Water Filtration provide EDI water systems deionised / demineralised & service, using both ion exchange and electro-deionisation (EDI). This is an electrically-driven water treatment technology that uses electricity, ion exchange membranes and resin to remove ionised species from water, which meets the highest water quality standards for most applications.
One Eight provides a full spectrum of water deionisation services for ultra pure water applications, ranging from large steam turbines to validated pharmaceutical systems. We are a full service provider with experienced 24/7 support and unmatched quality to ensure that you are guaranteed a continuous and reliable source of high purity water, designed specifically to meet your requirements.


Demineralised water is made by using ion exchange, electro-deionization, or membrane filtration technologies, which can be more efficient for creating ultrapure water than processes such as distillation (where water is boiled in a still and condensed, leaving dissolved contaminants behind).
Demineralisation by ion exchange, electro-deionization, or membrane filtration can produce water that is nearly 100% free of minerals and salts including (but not limited to):
Alkalinity (CO32-, HCO3–)
Calcium (Ca2+)
Chloride (Cl–)
Iron (Fe3+)
Magnesium (Mg2+)
Manganese (Mn2+)
Nitrate (NO3–)
Potassium (K+)
Silica (SiO2)
Sodium (Na+)
Sulfates (SO42-)
Depending on the technology used, the number of dissolved solids in water that has been demineralised can reach below 10 mg/l and the electrical conductivity can be less than 2 mS/m.
Using ion exchange or other processes using resins will not remove uncharged molecules, so while demineralisation can be counted on to remove almost all minerals and salts, the resulting water might contain some organic contaminants such as certain viruses or bacteria. Using reverse osmosis or nanofiltration to demineralise the water will remove these contaminants.
![]()
How is demineralised water beneficial for your factory/plant?
Demineralisation is typically reserved for applications requiring higher levels of water purity such as feed or makeup water for high-pressure boilers, rinse water for food & beverage industries, or process streams used in electronics manufacture.
The following list does not include every use for demineralised water, as it can be used for countless applications. It is, however, a representation of the most common applications, broken out by industry:
Power
In the power industry, demineralised water is often used for boiler feed water and steam generation. Boilers that generate steam to power turbines require high-pressure boilers and therefore more complex feed water treatment system to remove as many impurities as possible.
When steam is produced inside the boiler, the water particles collect and condense, then are recycled and used as part of the boiler feed water. Technically, the condensate that the steam-making process produces is distilled, but dissolved gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide are sometimes present. The chemical reactions due to the presence of these dissolved gases can cause severe corrosion on boiler pipes and parts. These gases are typically removed with demineralisation, advanced deaeration devices, or chemical scavengers. If you have these present, chances are your boiler feed water system will need to incorporate some form of these technologies.
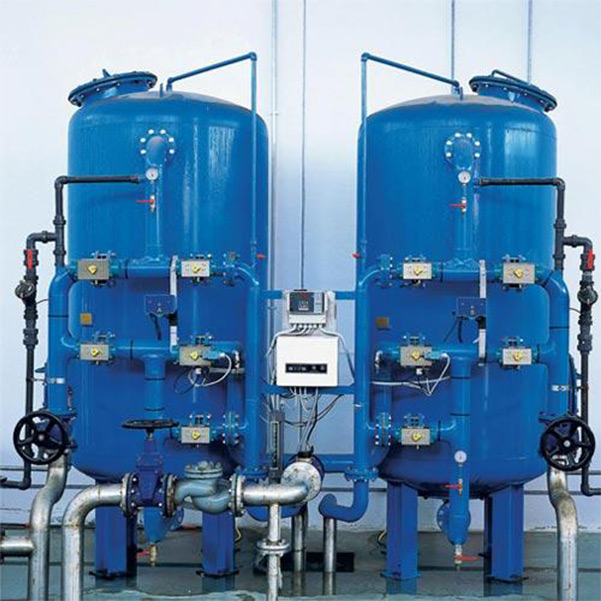
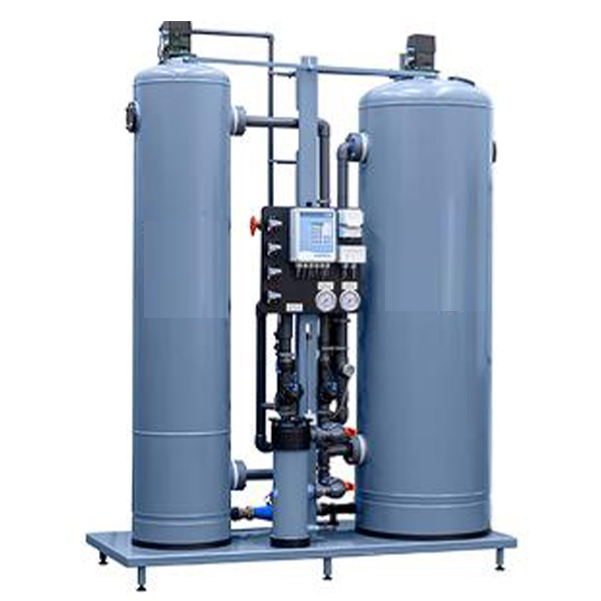


Refinery
Refineries use demineralised water, similar to the power industry, to feed their high-pressure boilers. Hardness and dissolved solids can wreak havoc on a facility’s equipment, and softening is often not enough treatment for most high-pressure boilers and process streams. Since many higher-pressure boilers require a higher quality of water with less contaminants than some lower-pressure boilers, demineralisation by ion exchange or membrane filtration (reverse osmosis or nanofiltration, mostly) is typically part of the water treatment process.
Petrochemical and Chemical
For the petrochemical and chemical industries, high-purity boiler feed water is also required. Demineralisation is used for this.
Demineralisation can also be used to treat cooling tower blowdown (which can also apply to other industries mentioned). If the water from your blowdown needs to be discharged, any discharge your system creates will need to meet all regulatory requirements. In certain areas where water is scarce, there could be large sewer connection fees, and demineralisation systems can be a cost-effective solution here, as they can help minimise the cost to connect to water and sewer lines. The discharge from your cooling tower bleed must also meet local municipal discharge regulations if your effluent is being returned to the environment or a publicly owned treatment works (POTW).
Food and Beverage
Demineralised water is often used to sanitise containers and equipment. It is also used in certain food processing applications, although membrane filtration is usually the technology used, so organic material, bacteria, viruses, etc., can be eliminated. Food and beverage production require ultrapure water at all parts of the manufacturing process due to quality regulations, so demineralisation is often part of the overall water treatment process.
Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Deionised and distilled water are used in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products and cosmetics in order to control product quality and safety. Different methods of producing demineralised water for different uses such as rinsing and cleaning will be reverse osmosis or deionisation, while formulations typically use distilled water.
Other industries
Demineralised water are both used for cleaning and rinsing applications across a wide variety of industries, including chemical production, mining, also, solvents in applications as diverse as electrocoating, where they function as a carrier for paint solids or in research labs where they may be used to make a variety of solutions.
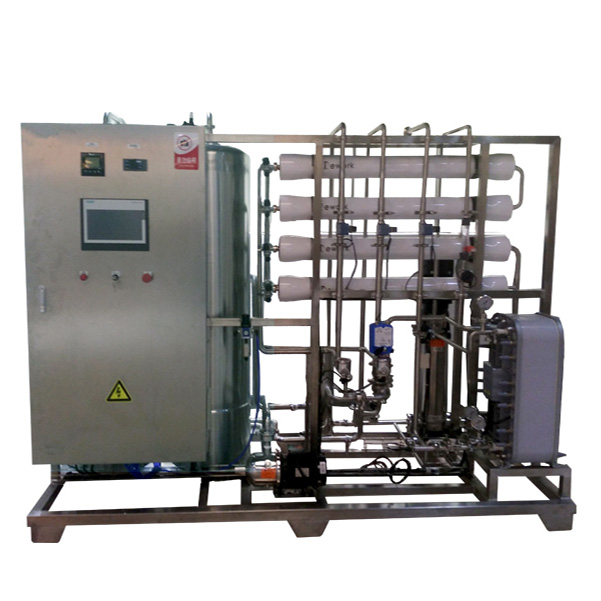


Contact Us
To find the best solution for your home or business, talk with one of our team today by filling in our form or calling us on +353 (0) 67 53 886
HEAD OFFICE
- Unit 17,
Springfort Business Park,
Nenagh,
Co Tipperary,
E45YK70 - +353 (0) 67 53 886
- info@oneeight.ie
For more information on our products, please do not hesitate in contacting us.