Introduction:
Water is a ubiquitous substance that plays a vital role in various industrial, laboratory, and everyday applications. However, not all water is the same. Deionized water, often abbreviated as DI water, is a specialised form of water with unique properties and applications. In this blog post, we’ll delve into what deionized water is, how it’s produced, its properties, and its diverse range of applications across different industries.
What is Deionized Water (DI Water)?
Deionized water, also known as demineralised water, is water that has had almost all of its mineral ions removed through a process called deionization. These mineral ions typically include calcium, magnesium, sodium, chloride, sulphate, and carbonate. Deionized water is essentially pure water, free from impurities that can interfere with various processes.
Production of Deionized Water:
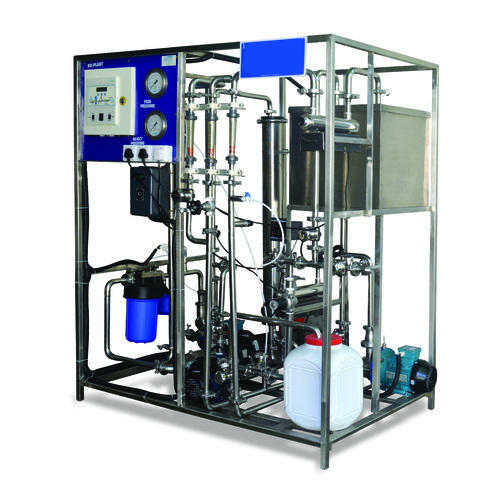
The production of deionized water involves the use of specialized equipment and techniques to remove mineral ions from regular water. The most common method of producing DI water is through ion exchange. In this process, water passes through ion exchange resins, which selectively remove ions from the water, replacing them with hydrogen and hydroxide ions. Another method involves membrane technologies such as reverse osmosis or electrodialysis, which physically separate ions from water molecules.
Properties of Deionized Water:
Deionized water exhibits several unique properties due to its purity:
- High Purity: DI water has extremely low levels of dissolved solids, making it highly pure.
- Neutral pH: It typically has a neutral pH of around 7, making it neither acidic nor alkaline.
- Lack of Conductivity: Since most of the mineral ions responsible for conductivity are removed, deionized water has very low conductivity.
- Lack of Taste and Odor: DI water is tasteless and odourless, as it lacks the minerals and impurities that contribute to taste and odour in regular water.
Applications of Deionized Water:
Deionized water finds widespread use across various industries and applications, including:
- Laboratory and Scientific Research: DI water is essential for preparing laboratory reagents, conducting experiments, and cleaning laboratory equipment where the presence of impurities could affect results.
- Electronics Manufacturing: It is used in the manufacturing of electronic components, printed circuit boards, and semiconductors for rinsing and cleaning to prevent mineral deposits that could interfere with electronic performance.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Industries: DI water is utilized in medical devices, pharmaceutical formulations, and laboratory analyses where water purity is crucial to ensure product quality and patient safety.
- Automotive Industry: It is employed in automotive cooling systems, battery maintenance, and parts cleaning to prevent mineral buildup and corrosion.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: Deionized water is used in the production of cosmetics, skincare products, and toiletries to maintain product stability and consistency.
- Boiler Feedwater: In industrial settings, DI water serves as feedwater for boilers to prevent scale formation and corrosion, ensuring efficient operation.
- Chemical Processing: It is employed in various chemical processes, such as manufacturing, cleaning, and rinsing, where the presence of impurities could interfere with reactions or product quality.
Conclusion:
Deionized water plays a crucial role in a wide range of industries and applications due to its high purity and unique properties. Whether in laboratories, manufacturing facilities, or everyday consumer products, DI water ensures the reliability, quality, and safety of countless processes and products. As technology advances and the demand for purity increases, the importance of deionized water in various sectors will continue to grow.
One Eight 067 53886 Info@OneEight.ie