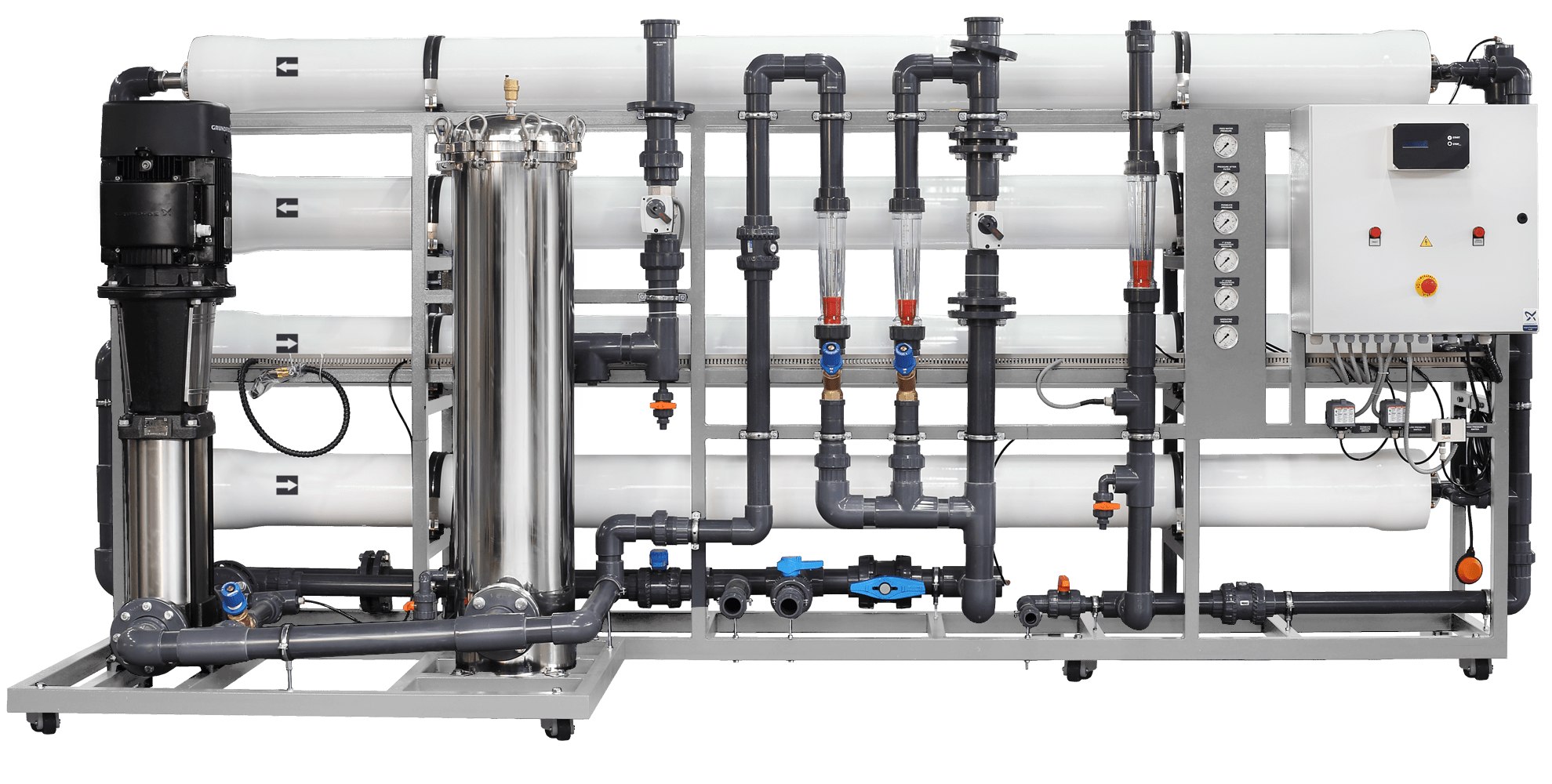
Reverse Osmosis systems form an integral part of most modern high specification water treatment, ensuring your commercial Reverse Osmosis (RO) system is working correctly is key to the successful operation and involves more detailed and frequent checks due to the larger scale and higher usage compared to residential systems. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
- Monitor Water Quality
– TDS Levels: Use a TDS meter to measure the Total Dissolved Solids levels of both the feed (incoming) water and the permeate (filtered) water. A well-functioning commercial RO system should achieve a TDS reduction of 90-99%.
– Water Testing: Conduct regular water tests for specific contaminants such as chlorine, lead, nitrates, and others based on your specific requirements. Consider third-party lab testing for more accurate results.
- Inspect and Maintain Filters and Membranes
– Pre-Filters: Check and replace pre-filters (sediment, carbon, etc.) regularly as per the manufacturer’s guidelines, typically every 3-6 months.
– RO Membrane: Inspect the RO membranes periodically and replace them as recommended (usually every 2-3 years) or if there is a noticeable drop in water quality.
– Post-Filters: Ensure post-filters are replaced on schedule to maintain water quality.
- Monitor System Pressure and Flow Rates
– Pressure Gauges: Regularly check the pressure gauges at different points in the system (feed water, pre-filter, post-filter, and permeate) to ensure they are within the specified range.
– Flow Meters: Use flow meters to monitor the flow rates of feed water, reject water, and permeate. A drop in permeate flow can indicate fouling or clogging.
- Check for Leaks and Integrity of Components
– Leaks: Inspect the system for any leaks, including connections, fittings, and the storage tank.
– Component Check: Regularly inspect pumps, valves, and other components for wear and tear or any signs of malfunction.
- Perform Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
– Scheduled Maintenance: Follow a strict maintenance schedule, including cleaning and sanitizing the system as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
– Chemical Cleaning: Periodically clean the RO membranes using appropriate cleaning chemicals to remove fouling and scaling.
- Monitor System Performance Metrics
– Salt Rejection: Calculate the percentage of salt rejection by comparing the TDS of feed water and permeate. A significant drop in salt rejection efficiency indicates membrane fouling or damage. Calculating salt rejection performance of the system will show the current performance. It is important performance to log in your operation records. Logging system performance will help to track the membrane quality and give you an indication of the membrane health and the overall performance of the system. The calculation based on feed and permeate conductivities.
Salt Rejection = (TDS Feed – TDS Product) / (TDS Feed) X 100
Example: 1,000 ppm – 42 ppm / 1,000 X 100 = 95.8% salt rejection
– Recovery Rate: Monitor the recovery rate (the percentage of feed water converted to permeate). Deviations from the expected recovery rate can signal problems. Recovery Rate means the amount of water that your system is producing expressed in percent. This is the ratio of permeate vs. the waste water (concentrate) dumped to drain. The higher the recovery rate the less concentrate dumped to drain. For example, if you have a 100 LPM feedwater flow and your concentrate flow is 25 LPM, this means that your system recovery is 75%. Calculating in LPM or Metric units RO system recovery can be found with this formula:
Permeate Flow / Feed Flow X 100 = % Recovery
- Automated Monitoring and Alarms
– Automation: Use an automated monitoring system with alarms to track critical parameters such as pressure, flow rate, TDS, and more. Set up alerts for any deviations from the normal operating range.
– Data Logging: Regularly log and analyse performance data to identify trends and potential issues early.
- Regular Professional Inspections
– Technician Visits: Schedule regular inspections and maintenance by qualified technicians to ensure all components are functioning correctly and to address any issues proactively.
– Compliance Checks: Ensure the system meets all regulatory and compliance standards for water quality and safety.
- End-User Feedback
– Water Taste and Odor: Gather feedback from users regarding the taste, odor, and appearance of the water. Any noticeable changes can indicate a problem with the system.
- System Documentation and Records
– Maintenance Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, filter and membrane replacements, water quality tests, and any issues or repairs.
– Operating Manual: Refer to the system’s operating manual for specific guidelines and troubleshooting tips tailored to your commercial RO system.
By diligently following these steps, you can ensure your commercial RO system operates efficiently, provides high-quality water, and maintains a long service life. Regular monitoring and proactive maintenance are key to preventing issues and ensuring optimal performance.